CI/CD, acronyms frequently used in DevOps, what is it? Stepping into DevOps, I wanted to know what it is. So here’s what I learned about it for everyone out there who wants to know too.
What is CI/CD?
Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery or Continuous Deployment is a way of continuously integrating all code from a team into a single codebase and is always delivery-ready. This is carried out for automated building, testing, and quicker delivery/deployment.
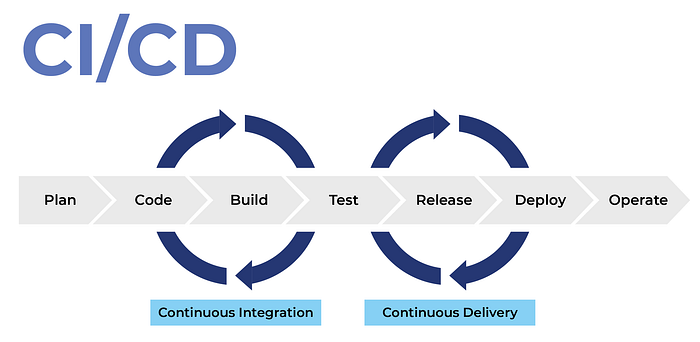
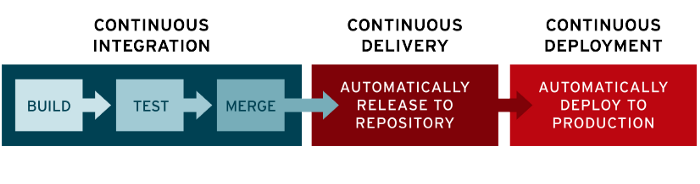
Continuous Integration vs. Continuous Delivery vs. Continuous Deployment
Continuous Integration is a development practice where developers integrate code into a shared repository several times a day i.e., every time a project team member commits changes to version control. With each integration, it is verified by an automated build, allowing teams to detect problems early. So, the more you integrate, the more quickly you can detect and locate the errors. This regular integration of new code into an existing codebase can be accomplished with automated tools that include the integrating and testing of the codebase.
Continuous Delivery is an extension of continuous integration as it automatically deploys all integrations or new code changes to a testing and/or a production environment after the build stage, always leaving a deployment-ready build artifact that has passed through a standardized test process in the hands of developers.
Continuous Deployment is a software release process that validates the changes made in a codebase using automated testing. It checks for stability for immediate deployment to a production environment for developers.
With continuous delivery, every code change is built, tested, and then pushed to a non-production testing or staging environment. There can be multiple, parallel test stages before a production deployment. The difference between continuous delivery and continuous deployment is the presence of a manual approval to update to production. With continuous deployment, production happens automatically without explicit approval.
Now, how do these terms relate to each other?
These “continuous” processes, combined, represent the end-to-end automation of the software build process where a team is always ready to deploy new integrations post automated tests. These processes have many benefits such as lower risk, fault isolations, faster release rate, easier maintenance & updates, better quality, lower cost, and happier teams. The goal is to build and deploy software as quickly as possible.
To put it simply continuous integration is part of both continuous delivery and continuous deployment. And continuous deployment is like continuous delivery, except that releases happen automatically.
These connected practices are often referred to as a “CI/CD pipeline” and are supported by development and operations teams working together in an agile way.
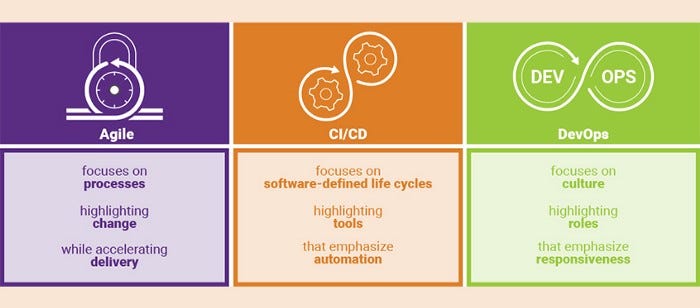
While Agile, CI/CD, and DevOps are different, they support one another. Agile focuses on the development process, CI/CD on practices, and DevOps on culture.
Hope this helped you understand better!
 Featurepreneur Articles
Featurepreneur Articles